NETWORK TOPOLOGY
NETWORK TOPOLOGY
3.More expensive because cost of the hub/switch
NETWORK TOPOLOGY
A network topology refers to the layout of the computers and devices in a communications network.
PHYSICAL TOPOLOGY
The arrangement of a cabling is the physical topology.
LOGICAL TOPOLOGY
The path that data travels between computers on a network is the logical topology.
Types of Network Topologies.
STAR TOPOLOGY
All the computers and other devices on the network
connect to a central device, thus forming a star.
Two types of devices that provide a common central connection point to all the other devices on the network are a hub and a switch.
The device that provides a common central connection point for other devices on a
network.
ADVANTAGES:
- If one device fails, only that device is affected.
- Devices can be added to or removed from network
- with little or no disruption.
- Easy to troubleshoot and isolate problem
DISADVANTAGES:
1.If the hub or switch fails, the entire network will be inoperable.
2.Requires more cable than most of the other topologies.
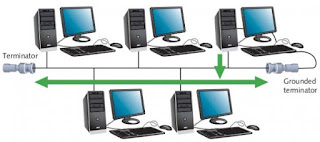
BUS TOPOLOGY
A bus network consists of a single central cable (backbone), to which all computers and other devices connect.
Bus topology uses coaxial cable as a backbone
The bus is the physical cable that connects the computers and other devices.
The bus in a bus network transmit data, instructions, and information as a series of signal.
Those signals are sent as electrical pulses that travel along the length of the cable in all directions
ADVANTAGES
1.Bus networks are inexpensive and easy to install.
2.Computers and other devices can be attached and detached at any point on the bus without disturbing the rest of the network.
3.Failure of one device usually does not affect the rest of the bus network.
DISADVANTAGES
1.There might be disruption when computer or other devices are added or removed.
2.Because all systems on the network connect to a single cable or backbone, a break in the cable will prevent all systems from accessing the network.
3.It is difficult to identify the problem if the entire network shut down.
RING TOPOLOGY
On a ring network, a cable forms a closed loop (ring) with all computers and devices arranged along the ring
•Data transmitted on a ring network travels from device to device around the entire ring, in one direction (clockwise or counterclockwise).
•Token passing is one method for sending data around a ring.
•Each device takes a turn sending and receiving information through the use of a token.
ADVANTAGES
1.The transmission of data is relatively simple as packets travel in one direction only.
2.Cable faults are easily located, making troubleshooting easier.
3.The uses of token passing enables all devices in a ring topology to share the network resources fairly.
1.A failure in any cable or device breaks the loop and can take down the entire network.
2.Data packets must pass through every computer therefore, this makes it slower.
A ring network can span a larger distance than a bus network, but it is more difficult to install




Comments
Post a Comment